
#Discount rate in discounted cash flow free
Today the 5 year T-bill yields 1.7%, the 10 year 2.2%, so a 2% risk free rate is a good proxy. A good proxy is a US government bond of a duration that’s commensurate with the time frame an investor would think of when owning the stock. If they conclude they won’t get this return they’ll sell the stock and the price will go down, if they conclude they’ll get more than this return additional investors will buy the stock and the price will go up, eventually driving the return to Ke in equilibrium. What investors expect to earn on their investment in the stock. The cost of equity, Ke, comes from the CAPM. Computing the Cost of Equity – The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) Simplifying this for Startupsįor most startups, equity is the primary method of financing, so it may be helpful to simplify things and state that WACC equals Ke (the cost of equity), which effectively also means that the Discount Rate should be equal to Ke. As described before, the proxy is book value. For a private company, best estimate – probably based on last round price. The right number to use is the marginal tax rate since you’re trying to make a marginal decision, and that’s typically 35% in the US. To be completely correct, it’s the coupon divided by the market value of debt, since the value of company bonds fluctuates, but generally this is too complicated for the exercise at hand and, unless the company is in distress, just looking at the book value is close enough. This is the average interest rate on the company’s debt. This comes from the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), described below. Because interest in debt is a pre-tax expense, the cost of debt is reduced by the tax rate (it’s effectively tax deductible). To calculate WACC, one multiples the cost of equity by the % of equity in the company’s capital structure, and adds to it the cost of debt multiplied by the % of debt on the company’s structure.

For most companies it’s just a weighted average of debt and equity, but some could have weird preferred structures etc so it could be more than just two components. There can be many sources of capital, and the weighted average of those sources is called WACC (Weighted Average Cost of Capital). The Discount Rate should be the company’s WACCĪll financial theory is consistent here: every time managers spend money they use capital, so they should be thinking about what that capital costs the company.
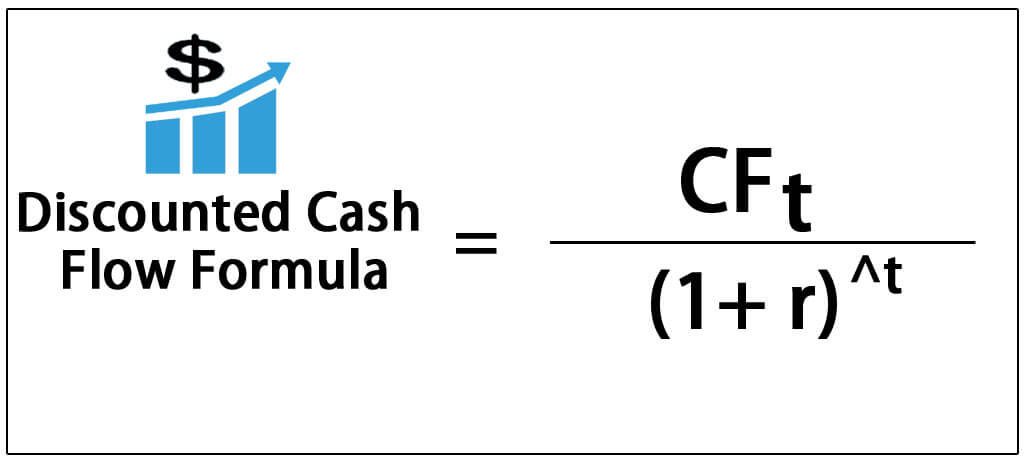
In the blog post, we suggest using discount values of around 10% for public SaaS companies, and around 15-20% for earlier stage startups, leaning towards a higher value, the more risk there is to the startup being able to execute on it’s plan going forward. This discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis requires that the reader supply a discount rate. In that blog post, we discuss why it is valuable to apply discounts to future cash flows when calculating the lifetime value of a customer (LTV). My thanks to my partner Stan Reiss, who co-authored this piece with me, providing all the expert math help. This post is a supplement to a blog post titled “ What’s your TRUE customer lifetime value (LTV)? – DCF provides the answer“.
#Discount rate in discounted cash flow how to
We look at how to compute the right discount rate to use in a Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
