

The radius resulting from is then 0.8 cm. The inside diameter is used for the calculation. The nominal diameter DN 15 therefore has an outside diameter of = 21,3 mm = 2,13 cm and an inside diameter of = 16 mm = 1,6 cm. A look at DIN EN 10255 or the nominal width tables of Wikipedia (GER) will help here. To determine the inner diameter and the resulting radius of a medium-weight pipe of DN 15, we have to look into a conversion table (or you know the values by heart). In the next step we calculate the pipe cross-sectional area, which is determined with Pi ( ) and the radius of the pipe. The volumetric flow rate thus amounts to 0.42 m³/h.
⇒ Divisor for conversion: 0.278 ⇒ x l/s / Divisor = y m³/h ⇒ Divisor for conversion: 3.6 ⇒ x m³/h / Divisor = y l/sġ liter/second = 3.6 cubic meters/hour ⇒ Divisor for conversion: 16.67 ⇒ x l/min / Divisor = y m³/hġ cubic meter/hour = 0.278 litres/second ⇒ Divisor for conversion: 0.06 ⇒ x m³/h / Divisor = y l/minġ liter/minute = 0.06 cubic meters/hour Important: The following applies to the conversion into cubic meters/hour or into liters/minute or liter/second:ġ hour = 3600 seconds ⇒ 3600 / 1000 = 3,6ġ cubic meter/hour = 16.67 liters/minute Since the volumetric flow rate is required in the unit m³/h, the result still has to be converted. medium-heavy pipe, nominal diameter: DN 15 according to DIN EN 10255įirst we calculate the volumetric flow rate with the following formula and then use the given values.What is the resulting flow velocity in the unit m/s?.How large is the pipe cross-sectional area in m²?.What is the volumetric flow rate with the given values in the unit m³/h?.To keep it simple we calculate this example in DN. In the US “NPS” (Nominal Pipe Size) is used. IMPORTANT: “DN” (Diameter Nominal) is used in europe and internationally. In a medium-heavy pipe with a nominal diameter of DN 15 (according to DIN EN 10255), 7 liters of water are to be conveyed in a period of one minute. Example Calculation – Volumetric Flow Rate and Flow Velocity Task In order to understand the topic a little better, I will show you in the following example calculations how you can use the formulas. Flow Velocity Formulaįlow velocity = volumetric flow rate / pipe cross-sectional area -> Example Calculations The flow velocity indicates the velocity of a flow in a pipe and is used for pipe flow calculations. The flow velocity is indicated differently in the literature. Volumetric flow rate= heat flow / density * specific heat capacity * temperature difference -> Flow Velocity Volumetric flow rate = pipe cross-sectional area * Flow velocity ->

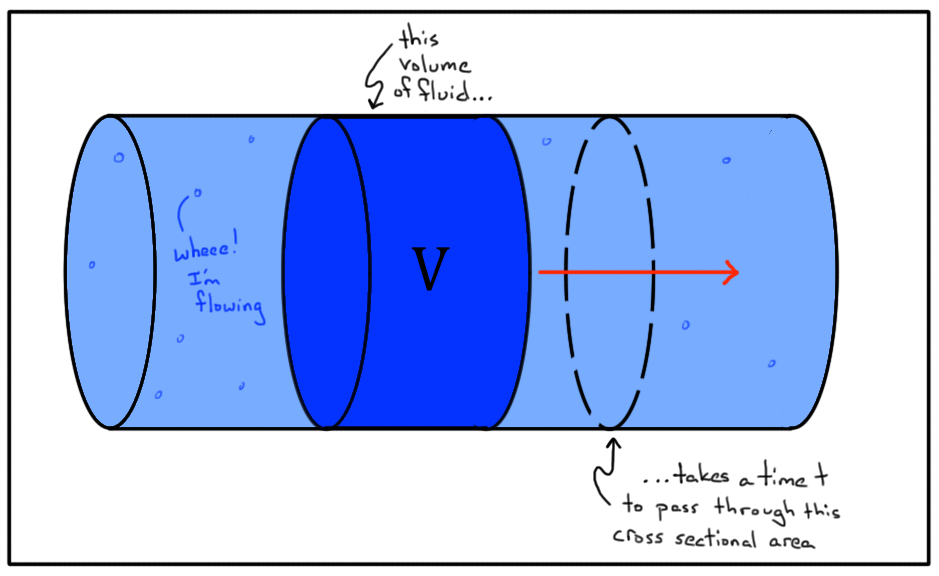
The following formulas will give you an overview: The volumetric flow rate can be calculated with the help of the volume and the time, with the pipe cross-sectional area and the flow velocity (small Omega), but also with the heat flow, the specific heat capacity, the density and the temperature difference. The unit of volumetric flow rate is cubic meters per hour or liters per hour. This question is asked in thermodynamics, because the volumetric flow rate is an important parameter for calculating the heat output of a radiator. “How much heating water flows through a heating system in a given time?” The question is therefore asked in relation to a heating system: The volumetric flow rate or indicates how much volume of a gas or liquid flows through a pipe or channel in a certain period of time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
